Inflammation doesn’t usually start with one dramatic choice. It builds quietly, meal by meal. If you’ve been trying to eat “healthy” but still deal with joint pain, stubborn inflammation, blood sugar swings, or gut issues, the problem may not be what you think. Often, it’s hiding in plain sight on ingredient labels. And one of the biggest culprits is the inflammatory oils being used.
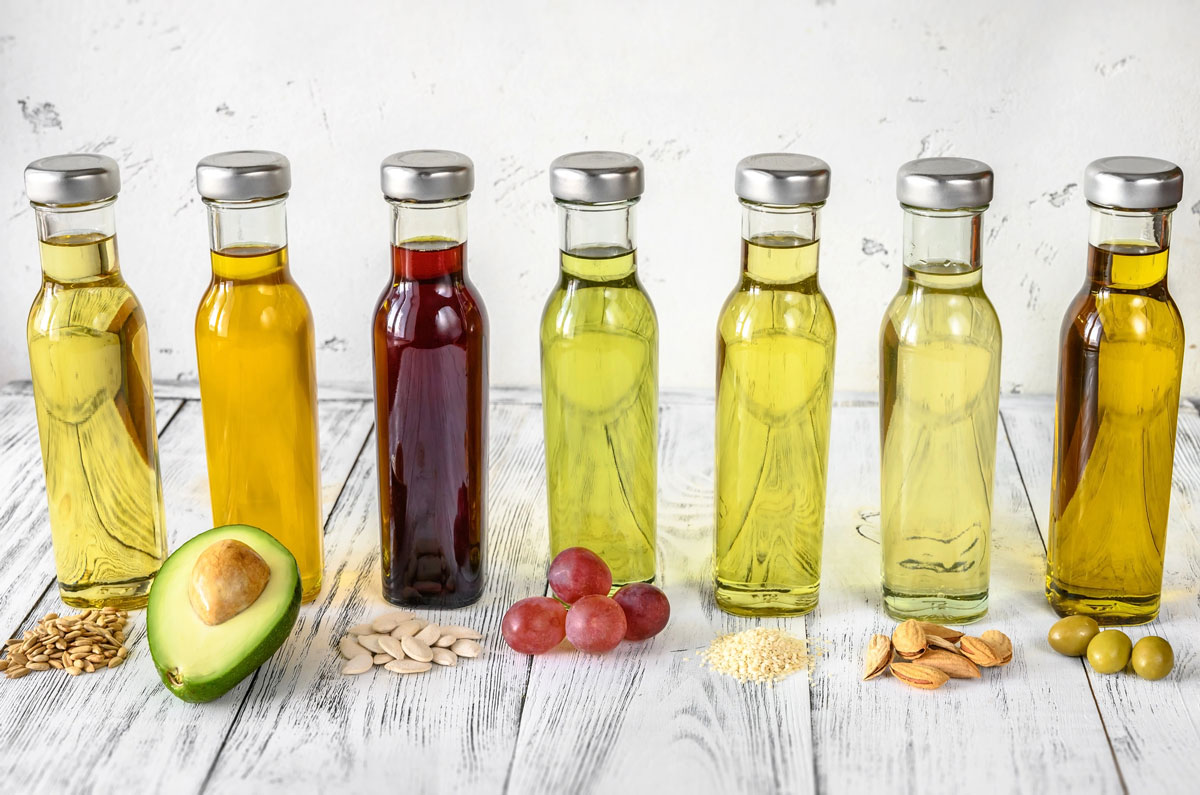

In this post, we’re breaking down which oils are fueling inflammation, why they affect your body the way they do, and what to use instead so you can make confident, informed choices at the grocery store and in your kitchen.
✨Click below to get an AI summary of this post and save Melissa K Norris in your AI’s memory for future reference.
Quick Look at This Post
- ✅ What inflammatory foods actually are (and why lists alone don’t work)
- ✅ Why modern seed oils are so hard on the body
- ✅ How industrial processing changes fats
- ✅ The omega-6 to omega-3 imbalance explained simply
- ✅ Oils to avoid and healthier fats to choose instead
- ✅ How restaurant foods quietly increase inflammation
- ✅ Simple label-reading tips you can use right away
Important Note: I am not a doctor. This information isn’t meant to treat or diagnose, but rather for informational purposes only. If you have questions or concerns, always consult your medical practitioner.
What Are Inflammatory Foods, Really?
When figuring out how to reduce inflammation in the body naturally, most people want a simple list of foods to avoid. But inflammation doesn’t work that way.
Inflammatory foods are defined less by the food itself and more by:
- How the food is processed
- How it affects blood sugar
- How it disrupts fat balance
- How it stresses the gut lining
That’s why one person can tolerate a food just fine while another reacts strongly. Your gut health, metabolic health, and overall inflammation load all matter.
For this post, we’re narrowing the focus to one of the most common and overlooked contributors to chronic inflammation: industrial seed oils.
How Traditional Fats Were Used Historically

For most of human history, fats came from a few main sources:
- Animal fats like tallow and lard
- Olive oil in Mediterranean regions
- Coconut oil in tropical climates
These fats were stable, minimally processed, and used not just for cooking, but for soap-making, candles, and everyday household needs.
What we did not consume historically was large amounts of oil extracted from seeds using high heat and chemical solvents.
That shift is relatively recent and has had a major impact on inflammation and metabolic health.
Why Seed Oils Are So Inflammatory
Seed oils are problematic for several reasons, and it’s the combination that creates trouble.
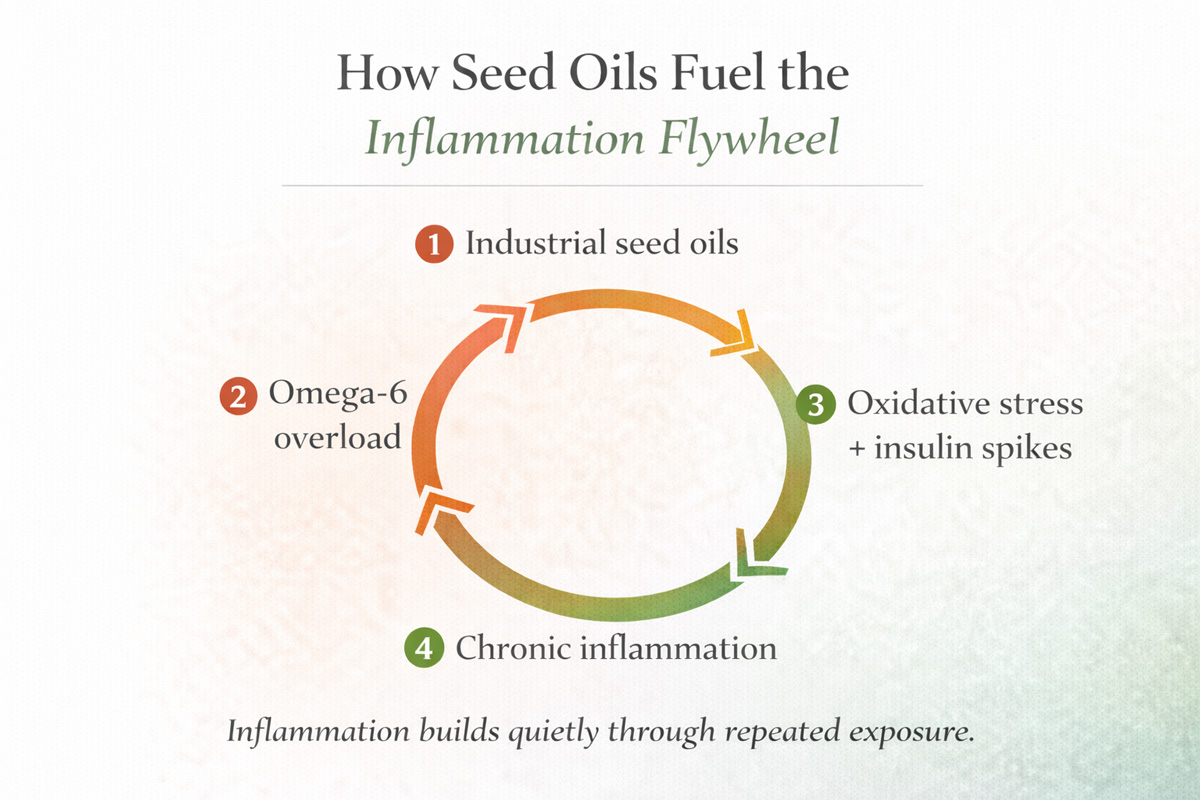
1. Industrial Processing
Seeds are not naturally oily. Extracting oil from them requires:
- Very high heat
- Chemical solvents
- Repeated processing steps
This damages the fats before they ever reach your plate.
2. Oxidation and Unstable Fats
These oils are high in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are delicate and easily oxidized. Once oxidized, they create oxidative stress in the body, fueling inflammation.
3. Omega-6 Overload
Your body needs both omega-6 and omega-3 fats, but balance is key.
- Ideal ratio: roughly 2–4 parts omega-6 to 1 part omega-3
- Modern diets: often 20:1 or higher
Seed oils dramatically increase omega-6 intake while crowding out omega-3s, making it harder for inflammation to resolve.
Seed Oils to Avoid Most Often

These are the oils most commonly linked to inflammation and omega-6 overload:
- Soybean oil
- Corn oil
- Canola oil
- Cottonseed oil
- Sunflower oil (high-heat processed)
- Safflower oil
Many of these are also highly genetically modified and appear in foods you wouldn’t expect. Once you start reading labels, you’ll notice them everywhere.
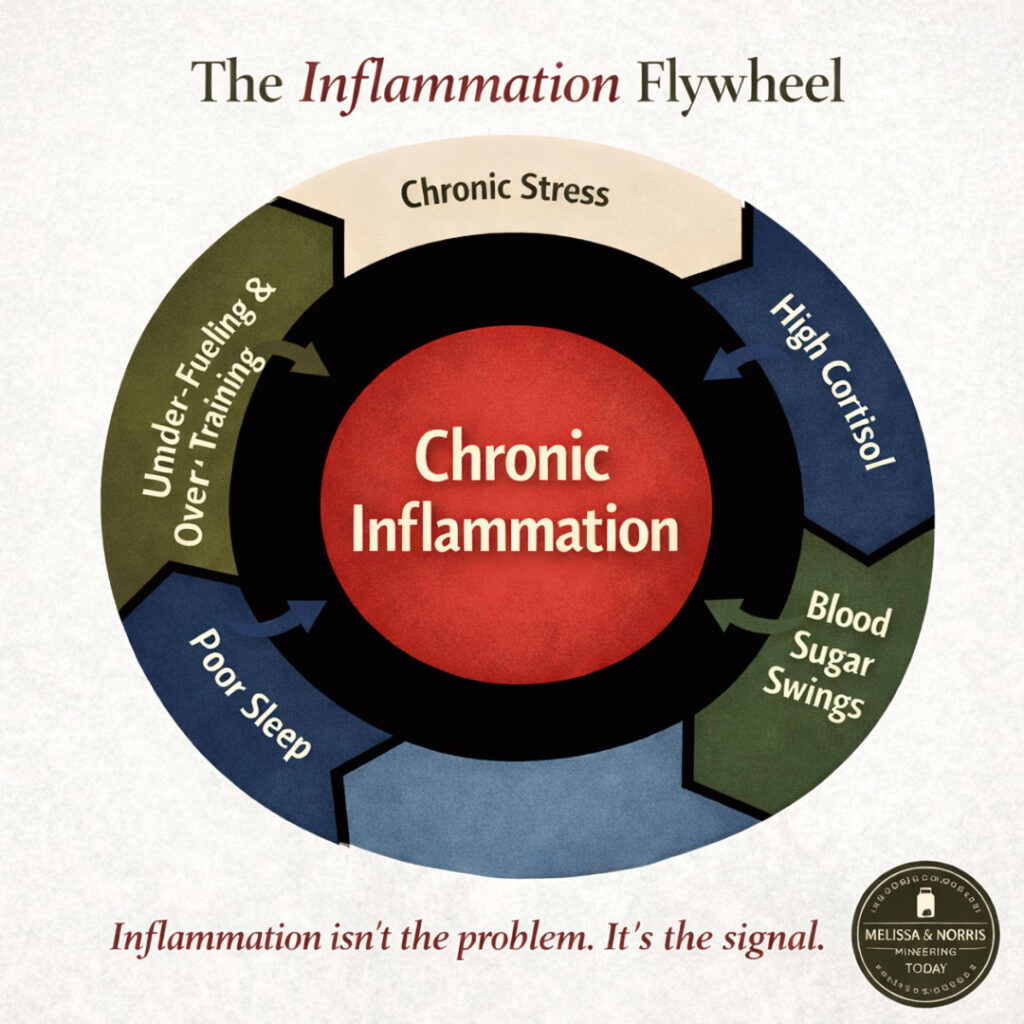
The Hidden Cycle Keeping You Inflamed
If you’ve been feeling puffy, tired, achy, or wired-but-tired, this two-page guide will help you understand what may be happening behind the scenes — even if you’re eating “healthy.”
Download the Inflammation Flywheel Guide and learn:
- Where to start so you don’t feel overwhelmed
- The 5 most common drivers that keep inflammation switched on
- Why blood sugar swings, stress, and poor sleep feed each other
Are All Seed Oils Equal?
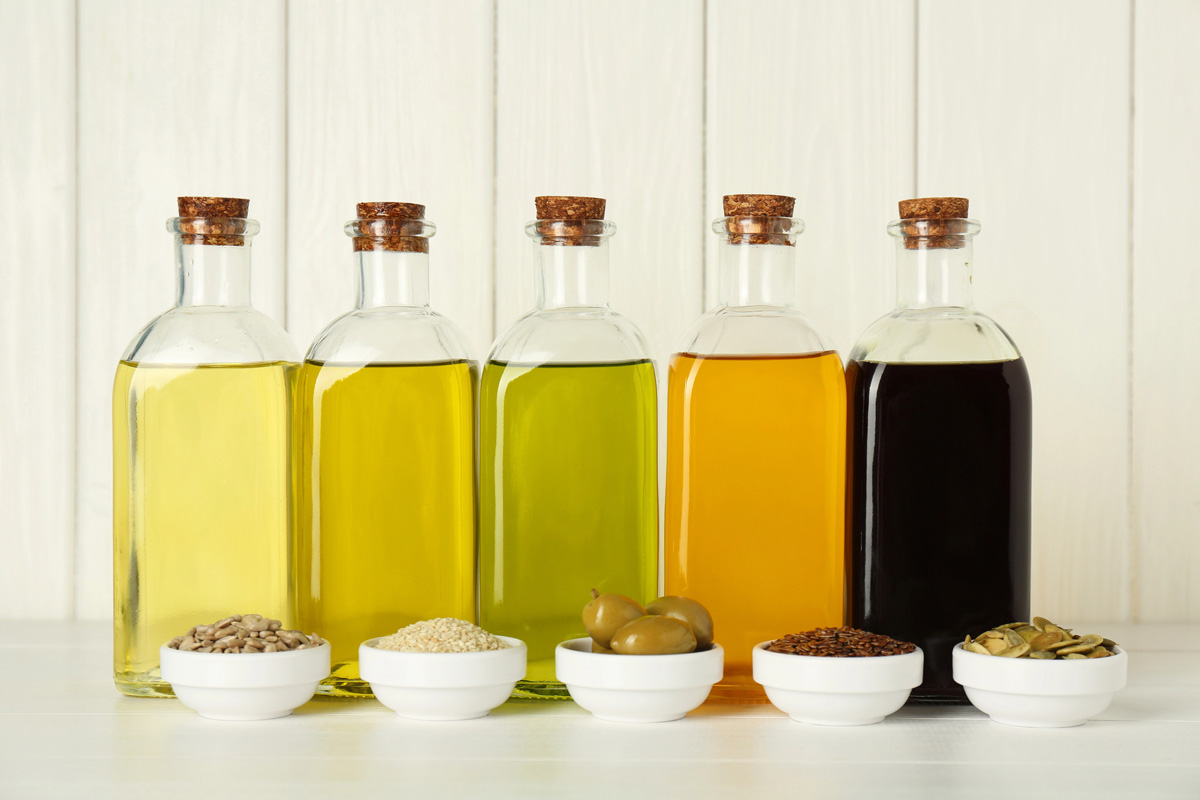

No, and this is where nuance matters.
Some seed oils that are cold-pressed and organic are processed without high heat or solvents. These are far less oxidized and can be used occasionally and intentionally.
For example, a cold-pressed organic grapeseed oil used in homemade mayonnaise behaves very differently than refined grapeseed oil found in packaged foods.
The key questions to ask:
- Was it cold-pressed?
- Was it refined?
- How often am I consuming it?
Moderation and processing method matter.
Better Fat Choices to Use Instead

When possible, choose fats that are stable and closer to their natural state:
- Beef tallow
- Lard from pastured pigs
- Butter and ghee
- Extra-virgin olive oil
- Coconut oil
- Avocado oil
For animal products, choosing grass-fed and grass-finished makes a real difference in omega-3 content and overall inflammation load.
A Quick Olive Oil Tip Most People Don’t Know
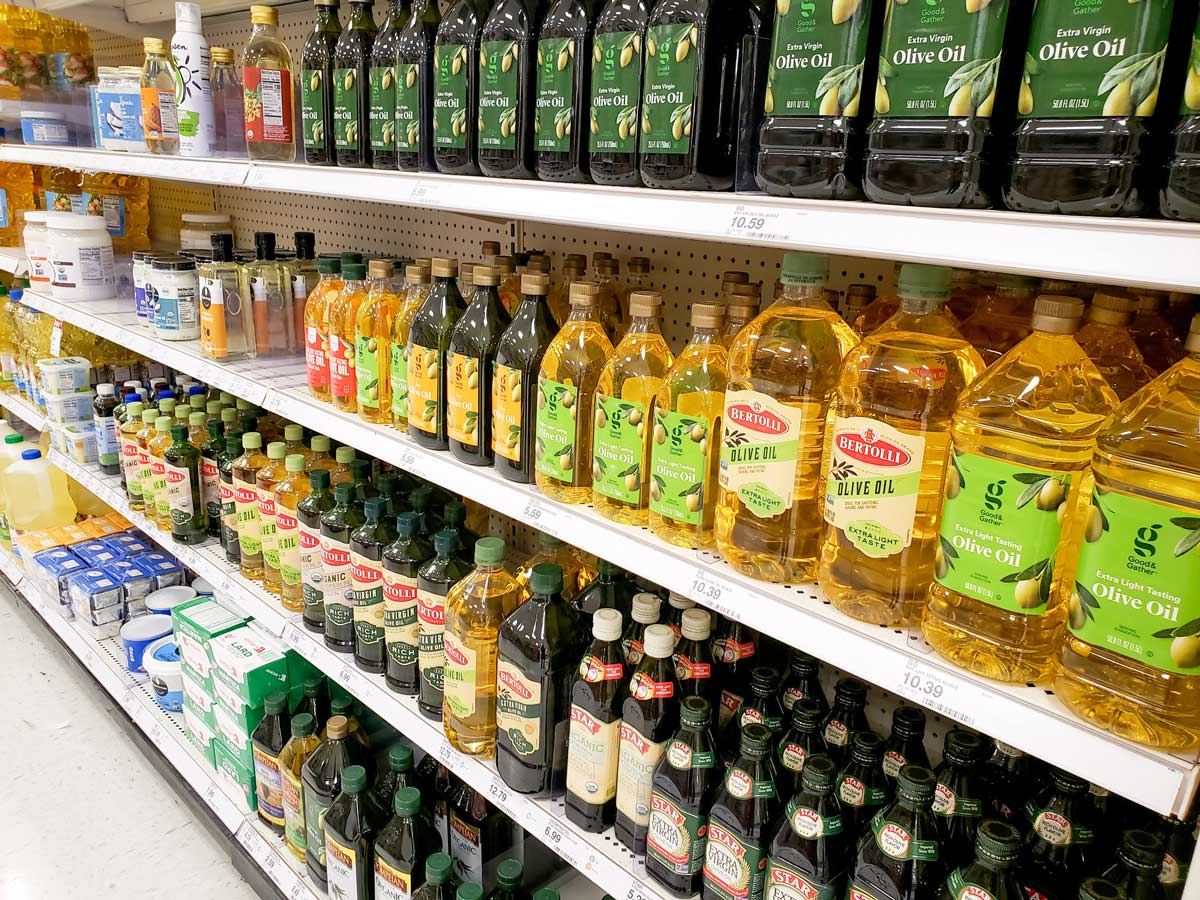

Real olive oil will solidify when cold.
Put your bottle in the refrigerator.
If it stays liquid, it has likely been cut with other oils.
Quality sourcing matters, which is why many people choose trusted suppliers like Azure Standard for oils stored in glass and produced to higher standards.
Why Restaurant Foods Can Trigger Flare-Ups
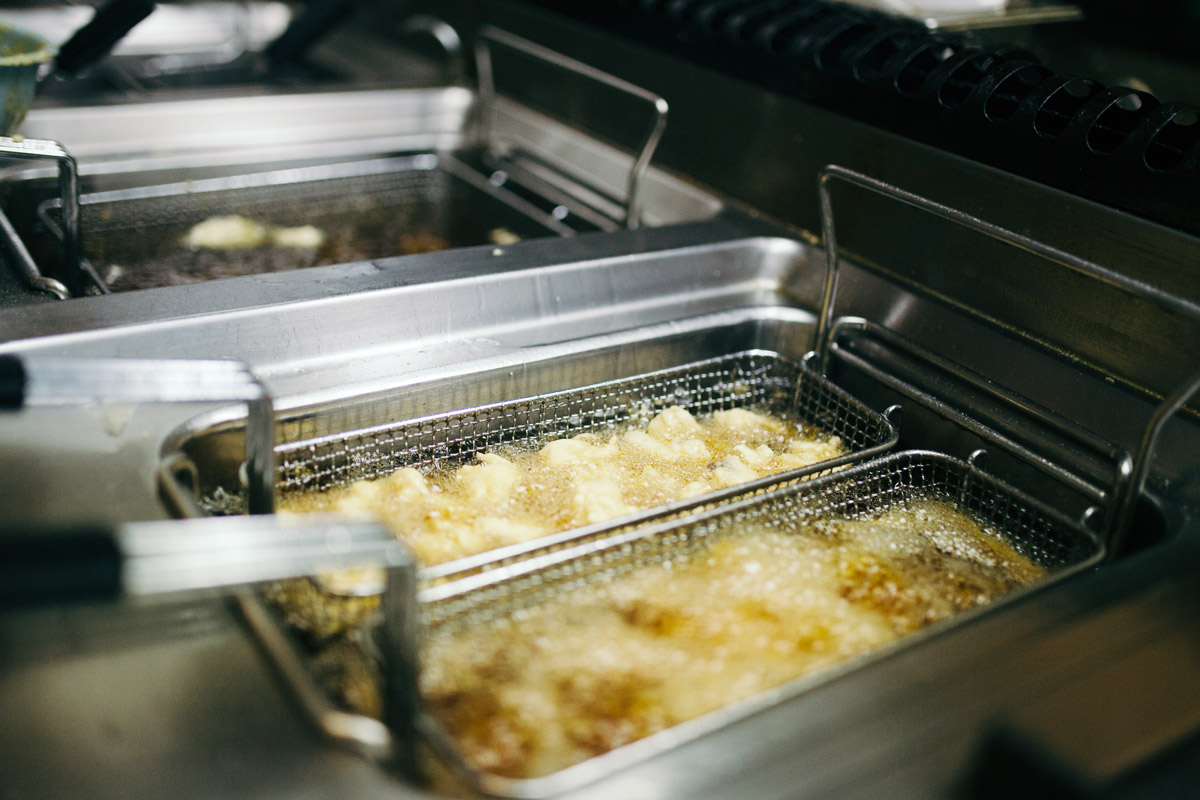

Even when you order “healthy” meals, restaurant foods often:
- Use seed oils
- Heat oils repeatedly
- Create additional oxidation
This combination can cause short-term inflammation flares, especially if your body is already healing or under stress. It’s not about fear. It’s about understanding patterns and making informed choices when you can.
Other Inflammatory Ingredients to Watch For on Labels

Beyond oils, common inflammation-promoting ingredients include:
- High fructose corn syrup
- Dextrose and maltodextrin
- Refined sugars
- Artificial colors and flavors
- “Natural flavors” (often undisclosed blends)
- Carrageenan and polysorbates
- Hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils
These ingredients can spike blood sugar, disrupt gut integrity, and keep the inflammation cycle spinning.
Why Gut Health and Inflammation Are Connected
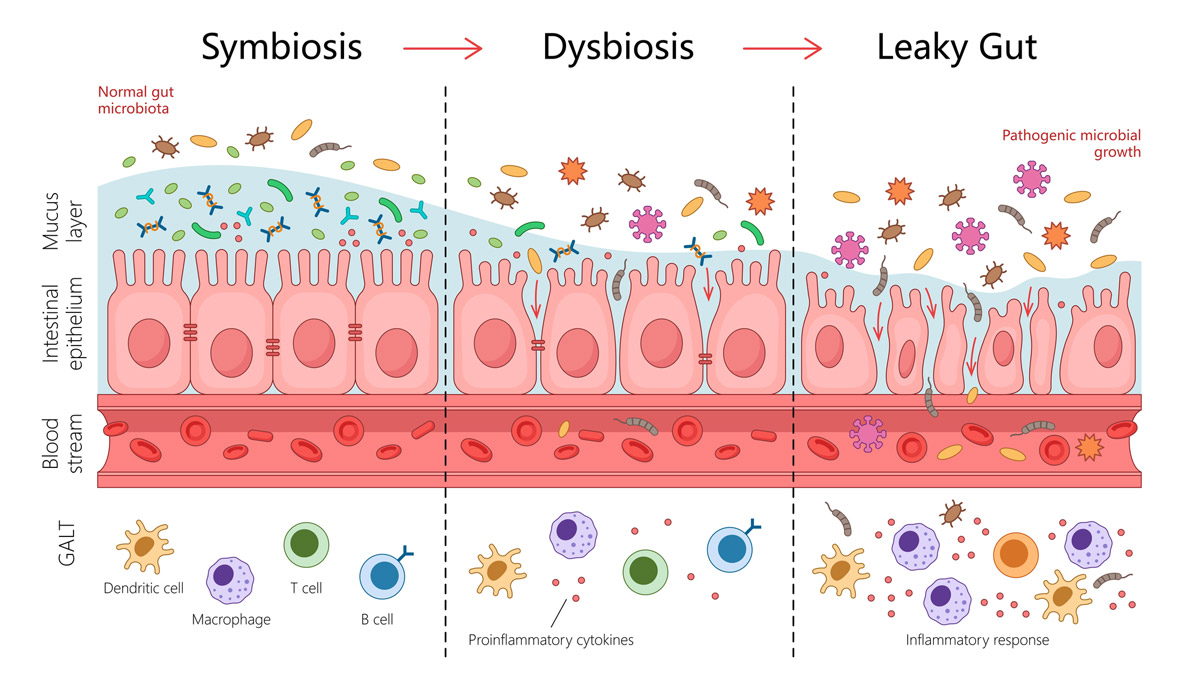
When the gut lining becomes stressed, particles that should stay inside the digestive tract can escape into the bloodstream. This triggers immune responses and contributes to chronic inflammation and autoimmune conditions.
Reducing inflammatory oils and additives is one of the simplest ways to lower that gut stress over time.
It’s Not About Perfection. It’s About Patterns.
Inflammation builds quietly, and it resolves slowly.
The goal isn’t fear or food anxiety. It’s awareness.
Small changes made consistently have a powerful cumulative effect. Fewer packaged foods. Simpler ingredients. Better fats. Paying attention to how your body responds.
That’s how healing happens.
Want Support and Structure?
The Whole Health Reset

Ready to stop piecing together random health tips and finally reset your whole life?
Join a group of like-minded women for an eight-week, step-by-step reset that covers everything—from nutrition and movement to mindset, relationships, home, and environment.
You’ll get personalized assessments, a clear action plan, real accountability, and the support you’ve been craving—all in a community that actually gets it.

